OVERVIEW
Infectious diseases are diseases in which tissue damage or dysfunction is produced by microorganisms. Despite the availability and use of effective vaccines and antibiotics, and improvement in sanitation ,infectious diseases remain an important health problem worldwide.
Five of the ten leading causes of death are infectious diseases , most of these deaths occur in children, with respiratory infections, infectious diarrhea, in addition to them malaria and TB continue to affect millions of peoples.
Contiguous mean person to person transmission.
Non contiguous acquired from sources such as animals, insects , soil, air or originating from normal microbial flora of the body.
Infectious agents: Infectious agents belong to a wide range of classes, they include:
1. Prions: which are modified host proteins lacking genetic molecules (RNA or DNA), it is not virus, e.g. prion that cause mad cow disease.
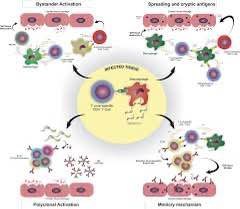
2. Viruses: obligate intracellular agent which ,depend on host in their replication ,composed of nucleic acid core (DNA or RNA) surrounded by a protein coat.
3. Bacteriophage and plasmid: mobile genetic elements that infect bacteria & indirectly causing human diseases by encoding bacterial virulence factors including adhesion, toxins and enzymes so this will convert nonpathogenic bacteria into virulent ones it make the bacteria resistance to antibiotics.
4. Bacteria: prokaryotes lacking nucleic acid and endoplasmic reticulum. They have cell wall made of 2 phospholipid bilayer. Two types of bacteria identified by their Gram stain properties: Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
5. Mycoplasma, rickettsiae, Chlamydia: These infectious agents are grouped together because they are similar to bacteria (they divided by binary fusion and susceptible to antibiotics) but lack certain structures.
6. Fungi: a primitive microorganism having a rigid cell wall, they are larger and more complex than bacteria and are eukaryotes. Thus, they possess nuclear membranes and cytoplasmic organelles, such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. There are two basic morphologic types of fungi: yeasts and hyphae.
7. Parasites: include:
· Protozoa (one celled parasites)
· Metazoa (Helminths) multi-celled parasites or worms.
· “Ecto-parasites, i.e., Anthrapodes.