- Introduction to computer System
A computer is an electronic device that can be programmed to accept data (input), process it and generate result (output). A computer along with additional hardware and software together is called a computer system.
A computer system primarily comprises a central processing unit (CPU), memory, input/output devices and storage devices.
A computer system comes in various forms and sizes. It can vary from a high-end server to personal desktop, laptop, tablet computer, or a smartphone.
Figure 1 shows the block diagram of a computer system. The directed lines represent the flow of data and signal between the components.
1.1 Central Processing Unit (CPU)
It is the electronic circuitry of a computer that carries out the actual processing and usually referred as the brain of the computer. It is commonly called processor also. Physically, a CPU can be placed on one or more microchips called integrated circuits (IC). The ICs comprise semiconductor materials.
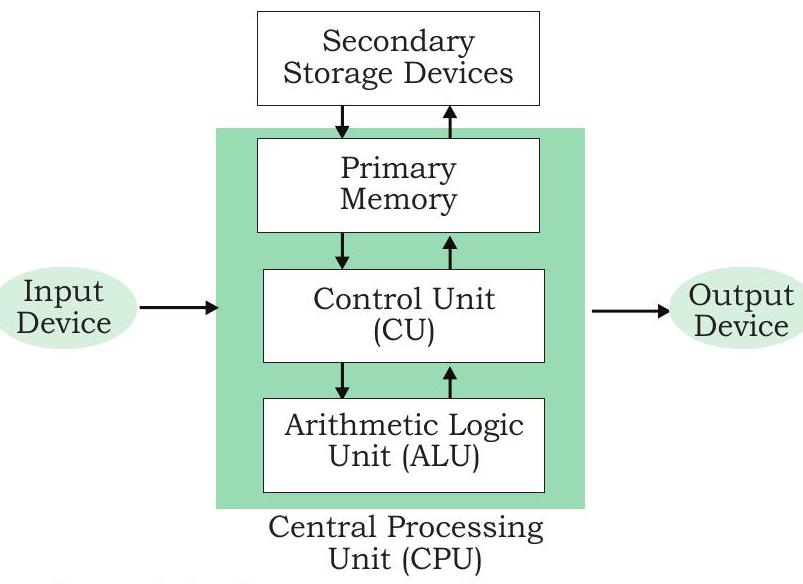
Figure 1: Components of a Computer System
The CPU is given instructions and data through programs. The CPU then fetches the program and data from the memory and performs arithmetic and logic operations as per the given instructions and stores the result back to memory. While processing, the CPU stores the data as well as instructions in its local memory called registers.
Registers are part of the CPU chip and they are limited in size and number. Different registers are used for storing data, instructions or intermediate results.
Other than the registers, the CPU has two main components: Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) and Control Unit (CU). ALU performs all the arithmetic and logic operations that need to be done as per the instruction in a program. CU controls sequential instruction execution. CPU is also popularly known as microprocessor.
