Lecturer
Protein Synthesis Inhibitors
A number of antibiotics exert their antimicrobial effects by targeting
bacterial ribosomes and inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Most of these
agents exhibit bacteriostatic activity.
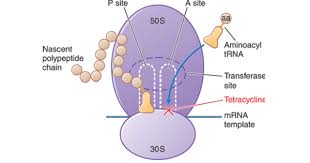
Bacterial ribosomes differ structurally from mammalian cytoplasmic
ribosomes and are composed of 30S and 50S subunits (mammalian
ribosomes have 40S and 60S subunits). The high concentrations of drugs
such as chloramphenicol or the tetracyclines may cause toxic effects as a
result of interaction with mitochondrial mammalian ribosomes, because
the structure of mitochondrial ribosomes more closely resembles bacterial
ribosomes.
Material File
