Lecturer
- Order Eimeriida contains five genera: Toxoplasma, Cryptosporidium, Cyclospora, Isospora and Sarcocystis
- Toxoplasma is an intracellular parasite that can cause congenital infections and also opportunistic infections (encephalitis) in HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infected patients
- Toxoplasma gondii
Toxoplasma gondii is an obligate intracellular parasite affecting a wide range of mammals and birds including humans.
- Morphology
It exists in three morphological forms—two asexual forms (tachyzoite and tissue cyst) and a sexual form (oocyst).
- Tachyzoite
- It is an actively multiplying form (trophozoite), usually seen in acute infection.
- Crescent shaped, having a pointed anterior end and a blunt posterior end.
- They can infect all mammalian (nucleated) cells except red blood cells (RBCs)
- the tachyzoites contain special organelles like rhoptries, and micronemes which are crucial for the adhesion and invasion into the host cell (Fig. 7.1A)
- Inside the host cell, tachyzoites are surrounded by a parasitophorous vacuole within which they divide asexually by a process called as internal budding or endodyogeny by which daughter trophozoites are formed within the parent cell.
- Host cell becomes distended by the proliferating tachyzoites and appears as pseudocyst. (Fig. 7.1B).
- Later on, the host cell ruptures releasing the tachyzoites that infects other cells.
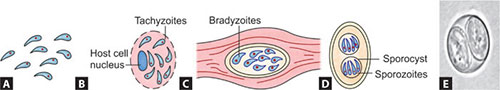
Figs 7.1A to E Toxoplasma gondii (schematic diagram); (A) tachyzoites; (B) pseudocyst; (C) tissue cyst; (D) sporulated oocyst; (E) sporulated oocyst in cat’s feces (saline mount).

Material File
